AZ-900 Guide: Security, responsibility, and trust in Azure
*This article could be a summary of content for learning purposes. For more information and knowledge, read the original articles in the References section.- Security responsibility is shared with Azure
- Identity management provides protection, even outside your network
- Encryption capabilities built into Azure can protect your data
- To protect your network and virtual networks
Cloud security is a shared responsibility
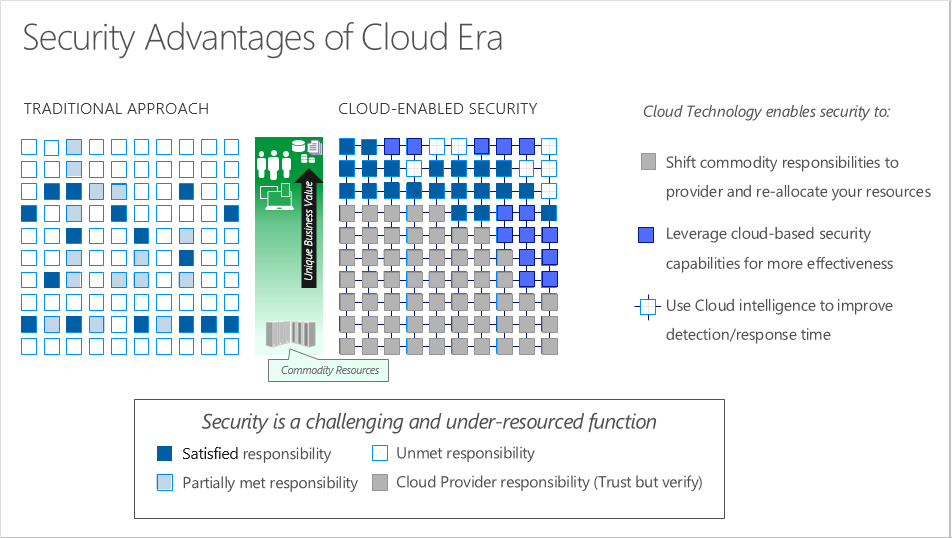
Security is a shared responsibility
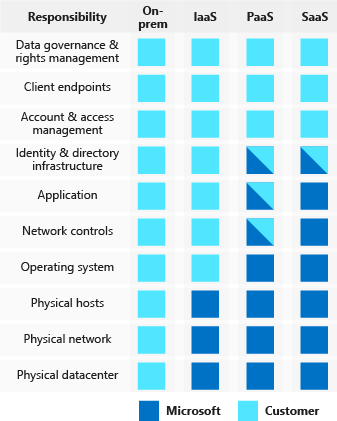
Regardless of the deployment type, you always retain responsibility for the following items:
- Data
- Endpoints
- Accounts
- Access management
A layered approach to security
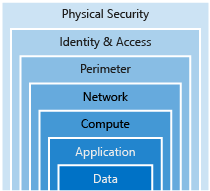
Data
In almost all cases, attackers are after data:
- Stored in a database
- Stored on disk inside virtual machines
- Stored on a SaaS application such as Office 365
- Stored in cloud storage
Application
- Ensure applications are secure and free of vulnerabilities.
- Store sensitive application secrets in a secure storage medium.
- Make security a design requirement for all application development.
Compute
- Secure access to virtual machines.
- Implement endpoint protection and keep systems patched and current.
Networking
- Limit communication between resources.
- Deny by default.
- Restrict inbound internet access and limit outbound, where appropriate.
- Implement secure connectivity to on-premises networks.
Perimeter
- Use distributed denial of service (DDoS) protection to filter large-scale attacks before they can cause a denial of service for end users.
- Use perimeter firewalls to identify and alert on malicious attacks against your network.
Identity and access
- Control access to infrastructure and change control.
- Use single sign-on and multi-factor authentication.
- Audit events and changes.
Physical security
- Physical building security and controlling access to computing hardware within the data center is the first line of defense.
Get tips from Azure Security Center
Available tiers
- Free. Available as part of your Azure subscription, this tier is limited to assessments and recommendations of Azure resources only.
- Standard. This tier provides a full suite of security-related services including continuous monitoring, threat detection, just-in-time access control for ports, and more.
Usage scenarios
- Use Security Center for incident response.
- Use Security Center recommendations to enhance security.
Identity and access
Authentication and authorization
- Authentication is the process of establishing the identity of a person or service looking to access a resource. It involves the act of challenging a party for legitimate credentials, and provides the basis for creating a security principal for identity and access control use. It establishes if they are who they say they are.
- Authorization is the process of establishing what level of access an authenticated person or service has. It specifies what data they’re allowed to access and what they can do with it.
What is Azure Active Directory?
Azure AD provides services such as:
- Authentication
- Single-Sign-On (SSO)
- Application management
- Business to business (B2B) identity services
- Business-to-Customer (B2C) identity services
- Device Management
Single sign-on
The more identities a user has to manage, the greater the risk of a credential-related security incident.
Multi-factor authentication
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) provides additional security for your identities by requiring two or more elements for full authentication. These elements fall into three categories:
- Something you know
- Something you possess
- Something you are
Providing identities to services
Service principals
A service principal is an identity that is used by a service or application. And like other identities, it can be assigned roles.
Managed identities for Azure services
When you create a managed identity for a service, you are creating an account on your organization’s Active Directory (a specific organization’s Active Directory instance is known as an “Active Directory Tenant”).
Role-based access control (RBAC)
Roles are sets of permissions, like “Read-only” or “Contributor”, that users can be granted to access an Azure service instance.

Privileged Identity Management
Encryption
What is encryption?
Symmetric encryption uses the same key to encrypt and decrypt the data.
Asymmetric encryption uses a public key and private key pair. Either key can encrypt but a single key can’t decrypt its own encrypted data. To decrypt, you need the paired key. Asymmetric encryption is used for things like Transport Layer Security (TLS) (used in HTTPS) and data signing.
Encryption at rest
Data at rest is the data that has been stored on a physical medium. This data could be stored on the disk of a server, data stored in a database, or data stored in a storage account.
Encryption in transit
Data in transit is the data actively moving from one location to another, such as across the internet or through a private network. Secure transfer can be handled by several different layers.
Encryption on Azure
Azure Storage Service Encryption for data at rest helps you protect your data to meet your organizational security and compliance commitments. With this feature, the Azure storage platform automatically encrypts your data before persisting it to Azure Managed Disks, Azure Blob storage, Azure Files, or Azure Queue storage, and decrypts the data before retrieval. The handling of encryption, encryption at rest, decryption, and key management in Storage Service Encryption is transparent to applications using the services.
Azure Disk Encryption is a capability that helps you encrypt your Windows and Linux IaaS virtual machine disks. Azure Disk Encryption leverages the industry-standard BitLocker feature of Windows and the dm-crypt feature of Linux to provide volume encryption for the OS and data disks. The solution is integrated with Azure Key Vault to help you control and manage the disk encryption keys and secrets (and you can use managed service identities for accessing Key Vault).
Transparent data encryption (TDE) helps protect Azure SQL Database and Azure Data Warehouse against the threat of malicious activity. It performs real-time encryption and decryption of the database, associated backups, and transaction log files at rest without requiring changes to the application. By default, TDE is enabled for all newly deployed Azure SQL Database instances.
Azure Key Vault is a centralized cloud service for storing your application secrets. Key Vault helps you control your applications’ secrets by keeping them in a single, central location and by providing secure access, permissions control, and access logging capabilities.
Overview of Azure certificates
Certificates used in Azure are x.509 v3 and can be signed by a trusted certificate authority, or they can be self-signed.
Types of certificates
- Service certificates are used for cloud services
- Management certificates are used for authenticating with the management API
Using Azure Key Vault with certificates
You can store your certificates in Azure Key Vault - much like any other secret. However, Key Vault provides additional features above and beyond the typical certificate management.
Automating certificate management helps to reduce or eliminate the error prone task of manual certificate management
Protect your network
A layered approach to network security
A layered approach provides multiple levels of protection, so that if an attacker gets through one layer, there are further protections in place to limit further attack.
Internet protection
Azure Security Center is a great place to look for this information, because it will identify internet-facing resources that don’t have network security groups associated with them, as well as resources that are not secured behind a firewall.
What is a Firewall?
A firewall is a service that grants server access based on the originating IP address of each request. You create firewall rules that specify ranges of IP addresses. Only clients from these granted IP addresses will be allowed to access the server. Firewall rules, generally speaking, also include specific network protocol and port information.
- Azure Firewall is a managed, cloud-based, network security service that protects your Azure Virtual Network resources.
- Azure Application Gateway is a load balancer that includes a Web Application Firewall (WAF) that provides protection from common, known vulnerabilities in websites. It is designed to protect HTTP traffic.
- Network virtual appliances (NVAs) are ideal options for non-HTTP services or advanced configurations, and are similar to hardware firewall appliances.
Stopping Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks
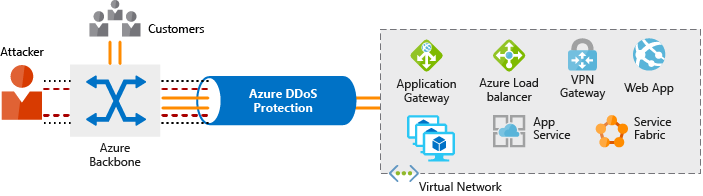
- Basic - The Basic service tier is automatically enabled as part of the Azure platform. Always-on traffic monitoring and real-time mitigation of common network-level attacks provide the same defenses that Microsoft’s online services use. Azure’s global network is used to distribute and mitigate attack traffic across regions.
- Standard - The Standard service tier provides additional mitigation capabilities that are tuned specifically to Microsoft Azure Virtual Network resources. DDoS Protection Standard is simple to enable and requires no application changes. Protection policies are tuned through dedicated traffic monitoring and machine learning algorithms. Policies are applied to public IP addresses associated with resources deployed in virtual networks, such as Azure Load Balancer and Application Gateway.
Controlling the traffic inside your virtual network
Virtual network security
Once inside a virtual network (VNet), it’s crucial that you limit communication between resources to only what is required. For communication between virtual machines, Network Security Groups (NSGs) are a critical piece to restrict unnecessary communication.
Network integration
Virtual private network (VPN) connections are a common way of establishing secure communication channels between networks. Connections between Azure Virtual Network and an on-premises VPN device are a great way to provide secure communication between your network and your VNet on Azure. To provide a dedicated, private connection between your network and Azure, you can use Azure ExpressRoute. ExpressRoute lets you extend your on-premises networks into the Microsoft cloud over a private connection facilitated by a connectivity provider.
Protect your shared documents
Microsoft Azure Information Protection (sometimes referred to as AIP) is a cloud-based solution that helps organizations classify and optionally protect documents and emails by applying labels.
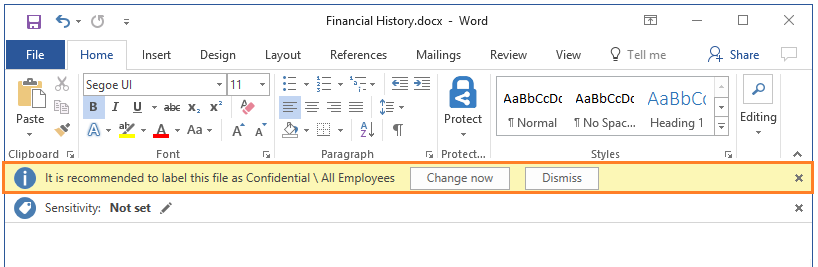
- Analyze data flows to gain insight into your business
- Detect risky behaviors and take corrective measures
- Track access to documents
- Prevent data leakage or misuse of confidential information
Azure Advanced Threat Protection
Azure Advanced Threat Protection (Azure ATP) is a cloud-based security solution that identifies, detects, and helps you investigate advanced threats, compromised identities, and malicious insider actions directed at your organization.
Azure ATP components
- Azure ATP portal: Azure ATP has its own portal, through which you can monitor and respond to suspicious activity. The Azure ATP portal allows you to create your Azure ATP instance, and view the data received from Azure ATP sensors. You can also use the portal to monitor, manage, and investigate threats in your network environment.
- Azure ATP sensor: Azure ATP sensors are installed directly on your domain controllers. The sensor monitors domain controller traffic without requiring a dedicated server or configuring port mirroring.
- Azure ATP cloud service: Azure ATP cloud service runs on Azure infrastructure and is currently deployed in the United States, Europe, and Asia. Azure ATP cloud service is connected to Microsoft’s intelligent security graph.
Purchasing Azure Advanced Threat Protection
Azure ATP is available as part of the Enterprise Mobility + Security E5 suite (EMS E5) and as a standalone license. You can acquire a license directly from the Enterprise Mobility + Security Pricing Options page or through the Cloud Solution Provider (CSP) licensing model. It is not available to purchase via the Azure portal.
Understand Security Considerations for Application Lifecycle Management Solutions
The Microsoft Security Development Lifecycle (SDL) introduces security and privacy considerations throughout all phases of the development process.
- Provide training
- Define security requirements
- Define metrics and compliance reporting
- Perform threat modeling
- Establish design requirements
- Define and use cryptography standards
- Manage security risks from using third-party components
- Use approved tools
- Perform Static Analysis Security Testing (SAST)
- Perform Dynamic Analysis Security Testing (DAST)
- Perform penetration testing
- Establish a standard incident response process
Summary
Defense in depth is the overriding theme - think about security as a multi-layer, multi-vector concern.
Check your knowledge
Cloud security is a shared responsibility between you and your cloud provider. Which category of cloud services requires the greatest security effort on your part?
Infrastructure as a service (IaaS)
Platform as a service (PaaS)
Software as a service (SaaS)
Which of these options helps you most easily disable an account when an employee leaves your company?
Enforce multi-factor authentication (MFA)
Monitor sign-on attempts
Use single sign-on (SSO)
Which of these approaches is the strongest way to protect sensitive customer data?
Encrypt data as it sits in your database
Encrypt data as it travels over the network
Encrypt data both as it sits in your database and as it travels over the network
There has been an attack on your public-facing website, and the application’s resources have been overwhelmed and exhausted, and are now unavailable to users. What service should you use to prevent this type of attack?
DDoS protection
Azure Firewall
Network Security Group
Application Gateway
You want to store certificates in Azure to centrally manage them for your services. Which Azure service should you use?
AIP
Azure AD
Azure Key Vault
Azure ATP
Related Posts
Quick Links
Legal Stuff

 Buy us a coffe
Buy us a coffe